Key Takeaways
-
Dogs bite their paws due to allergies, infections, injuries, anxiety, or grooming issues requiring immediate attention
-
Persistent paw biting can lead to secondary bacterial infections and worsen existing conditions if left untreated
-
Medical causes like pododermatitis, yeast infections, and nail problems are the most common triggers for paw biting behavior
-
Early veterinary intervention combined with proper paw care prevents complications and speeds recovery
-
Simple preventive measures like regular grooming, nail trimming, and paw cleaning significantly reduce paw biting incidents
Common Medical Causes of Paw Chewing and Biting
Medical conditions account for the majority of persistent paw biting cases. When dogs chew their paws excessively, they're typically responding to pain, irritation, or intense itching that demands relief. Understanding these medical triggers helps you recognize when your dog needs professional veterinary care.
Pododermatitis represents one of the most frequent medical causes of paw biting. This inflammatory condition affects paw pads, nail beds, and the spaces between your dog's toes. The inflammation creates redness, swelling, and often a foul odor that signals infection. Dogs develop pododermatitis from various triggers including allergies, bacterial overgrowth, or constant moisture from excessive licking. Managing allergies is crucial for reducing inflammation and preventing chronic paw issues.
Bacterial infections and yeast infections thrive in the warm, moist environment created by constant licking and chewing. Once established, these infections cause intense itching that compels dogs to continue biting their paws, creating a self-perpetuating cycle. Yeast infection particularly affects dogs with allergies, as the compromised skin barrier allows opportunistic organisms to flourish. A skin infection can develop from persistent paw chewing, especially if the dog's skin is already compromised.
Allergic reactions trigger some of the most intense paw biting episodes. Food allergies, seasonal allergies, and environmental allergens all manifest through itchy paws that drive dogs to chew for relief. In allergies dogs, an allergic reaction can be triggered by certain foods such as beef, chicken, dairy, and grains, leading to symptoms like itchy feet and paw chewing. Common food allergens include beef, chicken, dairy, wheat, and soy. Environmental triggers range from pollen and mold to cleaning products and lawn chemicals. The allergic itch creates an almost irresistible urge to chew, leading many dogs to create secondary infections through persistent biting. If a food allergy is suspected, a veterinarian may recommend a food trial to help diagnose which foods are causing the reaction and contributing to the paw chewing.
Injuries to the dog's paws prompt immediate and focused biting behavior. Cuts from sharp objects, paw burns from hot pavement, embedded foreign objects like thorns or grass seeds, and broken or torn nails all cause localized pain that dogs attempt to address through targeted chewing. A torn nail can cause significant discomfort and lead to focused paw chewing. These injury-related cases often show sudden onset of paw biting concentrated on specific toes or paw areas.
Environmental triggers can also include insect bites, such as those from fleas or mosquitoes, which cause irritation and lead to excessive itching and paw chewing.
When considering the anatomy of the paw, issues can occur between the dog's toes and on the dog's feet, which are common sites for irritation and paw chewing.
Parasites and Pest-Related Issues
External parasites create intense, localized itching that makes dogs bite their paws frantically. Fleas, ticks, and mites often concentrate around the paws where the skin is thinner and more accessible. Dogs with flea infestations frequently show excessive scratching and paw biting as they attempt to relieve the constant irritation.
Hookworm larvae present a particularly troublesome parasite issue. These microscopic pests burrow under the paw skin, creating painful tracks that drive dogs to persistent biting and chewing. The burrowing sensation combined with inflammatory response makes affected paws intensely uncomfortable.
Mites cause microscopic but severe irritation between the dog's toes and around nail beds. Sarcoptic mange mites and demodex mites both trigger intense itching that leads to destructive behavior including constant licking and biting of affected areas.
Year-round parasite prevention significantly reduces these pest-related triggers. Monthly preventatives that address fleas, ticks, and internal parasites help maintain healthy skin and reduce the likelihood of parasite-induced paw biting episodes.
Skin Conditions and Infections
Bacterial infections often develop as secondary complications from other causes of paw biting. When dogs chew their paws persistently, they break the skin barrier and introduce bacteria from their mouth into the wounds. These secondary infections create hotspots-painful, red, inflamed areas that make the original problem much worse.
Ringworm, despite its name being a fungal infection rather than a worm, causes ring-shaped patches of hair loss and scaling that dogs find intensely itchy. The circular lesions often appear between toes or on paw pads, creating targeted areas where dogs focus their chewing efforts.
Dry skin and dermatitis contribute to chronic paw biting, especially during winter months when indoor heating reduces humidity. The dog's skin becomes flaky and tight, creating an uncomfortable sensation that leads to increased licking and chewing. This moisture-seeking behavior often makes the problem worse by introducing bacteria and creating raw, irritated areas.
Interdigital cysts and blisters form between the dog's toes, creating painful pressure points that drive targeted biting behavior. These fluid-filled bumps often rupture from constant pressure and licking, leading to bacterial infections that require antibiotic treatment.
Behavioral and Psychological Triggers
Anxiety-induced paw biting represents a significant portion of chronic cases where no underlying medical cause exists. Anxious dogs often develop compulsive behaviors as self soothing mechanisms, and paw biting provides temporary stress relief through the release of endorphins. This neurochemical reward system can create addiction-like patterns where dogs continue biting even after the original stressor disappears. This is an example of self soothing behavior, where dogs lick or chew their paws to self soothe during stressful situations.
Separation anxiety frequently manifests through destructive behavior including excessive grooming and paw biting. Dogs left alone for extended periods may focus their anxiety energy on their paws, creating wounds and infections that require both medical and behavioral intervention.
Boredom and insufficient mental stimulation lead many dogs to develop problematic habits including persistent biting paws. Dogs bred for working purposes particularly need adequate physical exercise and mental challenges. Without appropriate outlets, they often redirect their energy toward repetitive behaviors like paw chewing. Providing chew toys can help redirect this energy and prevent compulsive paw chewing.
Environmental changes and stress responses can trigger temporary or chronic paw biting episodes. Moving homes, new family members, schedule changes, or loud noises like construction can all elevate stress levels and manifest through increased grooming behaviors that escalate into harmful paw biting.
Normal grooming behavior can gradually escalate into obsessive licking when dogs experience chronic stress or inadequate environmental enrichment. The transition from healthy self-care to compulsive behaviors often happens gradually, making early intervention crucial for preventing established behavioral patterns.
Calming supplements may help reduce anxiety and obsessive behaviors in some dogs, especially those with separation anxiety. However, they should be used alongside other behavioral interventions for best results. Which helps you now to answer the question. Why do dogs bite their paws?


Grooming and Maintenance Issues
Overgrown nails create constant pressure and discomfort that drives dogs to bite their paws seeking relief. When nails grow too long, they press into the paw pads during walking and standing, creating pain that dogs attempt to address through chewing. Regular nail trimming prevents this easily avoidable trigger for paw biting.
Matted fur between the dog's toes traps debris, moisture, and bacteria, creating irritated areas that become focal points for persistent chewing. The trapped material pulls on the skin and creates uncomfortable pressure that dogs try to relieve through biting and licking. Professional grooming or careful home maintenance prevents these mats from developing.
Improper nail trimming techniques can create splits, cracks, and infections that make paws painful and prone to biting. Cutting nails too short damages the quick, causing bleeding and long-term sensitivity. Using dull clippers crushes rather than cleanly cuts the nail, creating rough edges that snag and tear.
Hair growth between paw pads can become problematic when left untrimmed. Excessive hair collects debris and moisture, creating an environment where bacteria and yeast thrive. This trapped material causes constant irritation that leads to focused licking and chewing of specific paw areas.
Regular paw inspection during grooming sessions helps identify potential problems before they escalate into persistent biting behaviors. Keeping your dog's paws clean is essential to prevent infections and reduce the risk of licking and chewing caused by irritation or underlying health issues. Checking for cuts, embedded objects, nail damage, and early signs of infection allows for prompt treatment and prevents minor issues from becoming major problems.
Supporting Gut Health for Paw Health
A healthy gut is the foundation for your dog's overall well-being-including the condition of their paws. When your dog's digestive system is balanced, it can help reduce the risk of skin irritation, allergies, and the paw chewing that often follows. Feeding your dog a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality fiber, and probiotics supports gut health and can minimize the chances of itchy paws and excessive licking. Supplements like fish oil and probiotics not only promote a healthy digestive tract but also help reduce inflammation throughout your dog's body, including their skin and paw pads. By prioritizing gut health, you're taking a proactive step in preventing paw chewing and keeping your dog's paws comfortable and healthy.
Treatment Options and Veterinary Care
Veterinary attention becomes essential when paw biting persists beyond 24-48 hours or shows signs of infection including swelling, discharge, foul odor, or open wounds. Early professional intervention prevents complications and speeds recovery while addressing underlying causes that might not be obvious to pet owners. The goal of treatment is to stop chewing and prevent further damage to the paws.
Diagnostic procedures help veterinarians identify the specific cause of paw biting. Veterinarians will assess symptoms such as dog chewing paws and dog licking to determine the underlying cause. Skin scrapings detect mites and other parasites, bacterial cultures identify specific organisms causing infections, and allergy testing reveals environmental or food triggers. Advanced cases may require blood work to check for systemic conditions affecting the dog's skin health.
Medication options vary based on the underlying cause. Antibiotics address bacterial infections, while antifungal medications treat yeast infections and ringworm. Antihistamines and allergy medications help control allergic reactions, and pain medications provide relief for dogs with injuries or arthritis affecting their paws.
Topical treatments offer targeted relief for localized paw problems. Medicated shampoos containing antimicrobial agents help control surface bacteria and yeast. Prescription sprays and ointments deliver medications directly to affected areas while providing barrier protection against further damage.
Advanced treatments for chronic conditions may include immunotherapy for severe allergies, specialized dietary trials for food sensitivities, and behavioral medications for anxiety-driven compulsive behaviors. These comprehensive approaches address complex cases where simple treatments haven't provided adequate relief.
Home Care and Management Strategies
Proper paw cleaning after outdoor activities removes allergens, irritants, and debris that trigger biting episodes. Use pet-safe wipes or gentle solutions to clean between toes and around paw pads. Regularly check your pup's paws for signs of irritation, redness, or allergic reactions, especially between the toes and on the paw pads. Thorough drying prevents moisture-related bacterial and yeast overgrowth that complicates existing problems.
Protective barriers like dog booties, breathable socks, or recovery cones prevent dogs from accessing their paws during healing periods. These tools break the lick-bite cycle and allow damaged tissue to recover while medications take effect. Remove barriers during supervised activities to prevent stress and ensure normal mobility.
Environmental modifications reduce exposure to allergens and irritants that trigger paw biting. Use pet-safe cleaning products, avoid lawn chemicals during peak allergy seasons, and provide indoor alternatives during extreme weather when hot pavement or ice-melting chemicals pose risks to paw pads.
Dietary changes benefit dogs with food allergies causing paw issues. Veterinary-supervised elimination diets systematically remove potential allergens while monitoring for improvement. Novel protein sources and limited ingredient formulas help identify and avoid problematic foods that trigger allergic reactions.
Safe home remedies supplement veterinary treatment but should never replace professional care. Cool compresses provide temporary relief for inflamed paws, while paw balms protect dry or cracked paw pads. Always consult your veterinarian before applying any products to ensure they won't interfere with prescribed treatments.
Alternative Therapies for Paw Chewing
If your dog struggles with persistent paw chewing or irritated paws, alternative therapies may offer additional relief alongside traditional treatments. Acupuncture can help reduce pain and inflammation by stimulating blood flow to affected areas, while massage therapy eases tension and promotes relaxation-especially helpful for anxious dogs. Herbal remedies, such as calendula or diluted tea tree oil, may soothe and calm irritated paws when used appropriately. Always consult your veterinarian before starting any alternative therapies to ensure they are safe and suitable for your dog's specific needs. These holistic approaches can be valuable tools in managing paw chewing and supporting your dog's overall comfort.

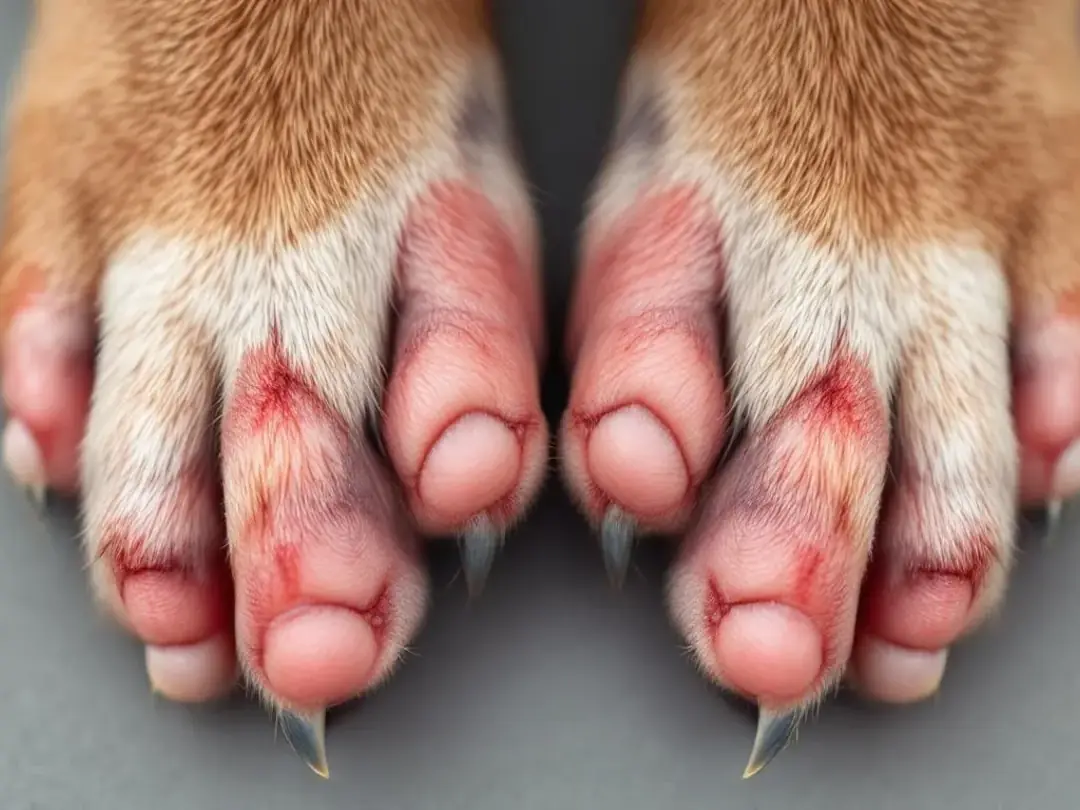
Prevention and Long-term Management
Regular paw inspection creates a routine that catches problems before they escalate into persistent biting behaviors. Check paws weekly for cuts, embedded objects, nail damage, swelling, or early signs of infection. Also, watch for signs of your dog licking their paws excessively, as this can indicate underlying issues with the dog paw such as allergies, infections, or injuries. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and prevents minor issues from becoming major problems requiring extensive intervention.
Proper nail trimming schedules maintain optimal paw health and prevent overgrowth-related discomfort. Most dogs need nail trims every 2-4 weeks, depending on activity level and nail growth rate. Learn proper techniques or establish relationships with professional groomers who can maintain appropriate nail length consistently.
Environmental protection strategies shield paws from common hazards that trigger biting episodes. Use dog booties on hot pavement, rinse paws after exposure to de-icing chemicals, and avoid walking in areas treated with lawn chemicals or fertilizers. Protecting your dog paws from these hazards can prevent injury and reduce the risk of paw chewing. These simple precautions prevent many injury and irritation-related paw biting cases.
Allergen avoidance and seasonal allergy management help sensitive dogs avoid triggers that lead to intense itching and paw biting. Monitor pollen forecasts during peak seasons, use air purifiers indoors, and work with veterinarians to develop preventive treatment plans for dogs with known environmental allergies.
Exercise and mental stimulation address behavioral causes of paw biting by providing appropriate outlets for energy and stress. Regular walks, interactive toys, training sessions, and puzzle feeders help prevent boredom-related destructive behaviors including obsessive licking and paw chewing.
Building Healthy Paw Care Habits
Daily paw cleaning routines remove potential irritants before they cause problems. Wipe paws with pet-safe products after walks, especially in urban environments or during allergy seasons. Focus on areas between toes where debris commonly accumulates and creates irritation.
Maintaining appropriate paw hair length through regular trimming prevents matting and debris accumulation. Use blunt-tip scissors or electric clippers designed for pet grooming to carefully trim excess hair between paw pads and around toes. Professional groomers can demonstrate proper techniques for nervous pet owners.
Paw balms and moisturizers protect dry or cracked paw pads from environmental damage while maintaining healthy skin barrier function. Apply products designed specifically for dogs, as human lotions may contain ingredients toxic to pets. Focus application on paw pads rather than between toes where moisture can promote bacterial growth.
Consistent grooming schedules with professional services ensure comprehensive paw care including nail trimming, hair maintenance, and early problem detection. Establish relationships with groomers who understand your dog's specific needs and can provide continuity of care over time.
Creating positive associations with paw handling through training helps dogs accept necessary care without stress. Practice gentle paw touching during calm moments, reward cooperation with treats, and gradually increase handling duration. This foundation makes medical examinations and home care much easier when problems arise.
Creating a Safe Environment for Your Dog
Your dog's environment plays a big role in preventing paw chewing and destructive behavior. Start by removing hazards like sharp objects, toxic substances, and hot surfaces that can injure or irritate your dog's paws. Make sure your dog's living space is clean, comfortable, and free from stressors that might trigger anxiety or boredom. Providing plenty of exercise, interactive toys, and mental stimulation helps channel your dog's energy in positive ways, reducing the urge to chew their paws out of frustration or boredom. By creating a safe and enriching environment, you help protect your dog from paw problems and encourage healthy, happy behavior.
Recognizing Signs of Infection
Spotting the early signs of infection is crucial when your dog is licking or chewing their paws excessively. Watch for symptoms like redness, swelling, discharge, or a strong, unpleasant odor coming from your dog's paws-these are clear indicators that an infection may be present. If you notice any of these signs, or if your dog seems to be in pain, limping, or constantly licking the same area, it's important to seek veterinary attention promptly. Your veterinarian can diagnose the issue and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include antibiotics, topical medications, or other interventions. Acting quickly helps prevent the infection from worsening and ensures your dog's paws heal properly, keeping them comfortable and active.
When Professional Help is Necessary
Immediate veterinary intervention becomes essential when dogs show signs of serious paw problems including persistent bleeding, severe swelling, discharge with foul odor, or inability to bear weight on affected paws. These symptoms indicate infections, injuries, or systemic conditions requiring prompt professional treatment to prevent complications.
Chronic cases lasting more than two weeks despite home care efforts need specialized dermatological evaluation. Persistent paw biting often involves complex underlying causes that require advanced diagnostic testing and targeted treatment protocols beyond basic first aid measures.
Behavioral modification programs address anxiety-related paw biting through systematic desensitization and counterconditioning techniques. Veterinary behaviorists or certified trainers can develop customized programs that address specific triggers while teaching alternative coping mechanisms for anxious dogs.
Working with certified dog trainers helps modify compulsive behaviors through structured training protocols. These professionals can identify environmental triggers, develop management strategies, and teach owners how to redirect problematic behaviors toward appropriate outlets.
Long-term management strategies for dogs with recurring issues require ongoing professional support to monitor progress, adjust treatments, and prevent relapse. Regular check-ups allow veterinarians to modify treatment plans based on seasonal changes, life stage transitions, and evolving health needs.
FAQ
How long should I wait before seeing a vet if my dog starts biting their paws?
If paw biting persists for more than 24-48 hours or if you notice swelling, discharge, or open wounds, schedule a veterinary appointment immediately. Early intervention prevents secondary infections and speeds recovery.
Can I use human antiseptics or medications on my dog's paws?
Never use human medications like hydrogen peroxide, Neosporin, or Benadryl without veterinary approval. Many human products are toxic to dogs and can worsen paw conditions or cause additional health problems.
Will my dog's paw biting stop on its own?
While occasional paw licking is normal, persistent biting rarely resolves without addressing the underlying cause. Untreated conditions typically worsen and can lead to secondary bacterial infections, making treatment more complex and expensive.
Is it safe to use an Elizabethan collar for extended periods?
E-collars are safe for temporary use but should be removed during meals and supervised activities. Long-term use requires veterinary guidance to ensure your dog can eat, drink, and rest comfortably while the paws heal.
Can diet changes help reduce paw biting in dogs?
Yes, if food allergies are the underlying cause. Common allergens include beef, chicken, dairy, wheat, and soy. A veterinary-supervised elimination diet lasting 8-12 weeks can identify problematic ingredients and significantly reduce allergic paw biting.





